Draw the line structure for ch3coh ch2ch3 2 – Delving into the line structure of CH3COH CH2CH3 2, we embark on a scientific exploration that unravels the intricacies of this organic compound. Its structural formula, functional groups, isomerism, physical properties, chemical reactions, and applications will be meticulously examined, providing a comprehensive understanding of its nature and behavior.
Composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms, CH3COH CH2CH3 2 exhibits a unique molecular architecture that governs its chemical properties and reactivity. This colorless liquid possesses a characteristic odor and finds diverse applications in various industries, making it a compound of both scientific and practical significance.
1. Structural Formula: Draw The Line Structure For Ch3coh Ch2ch3 2
The line structure of CH3COH CH2CH3 2 is as follows:
CH3 – C (= O) – CH2 – CH3
This structure represents a ketone functional group, with a carbon-carbon double bond and a carbon-oxygen double bond.
2. Functional Groups
Ketone Group, Draw the line structure for ch3coh ch2ch3 2
The ketone group is the primary functional group in CH3COH CH2CH3 2. Ketones are characterized by a carbon-carbon double bond and a carbon-oxygen double bond. The carbonyl group (C=O) is polar, making ketones reactive and susceptible to nucleophilic attack.
3. Isomerism
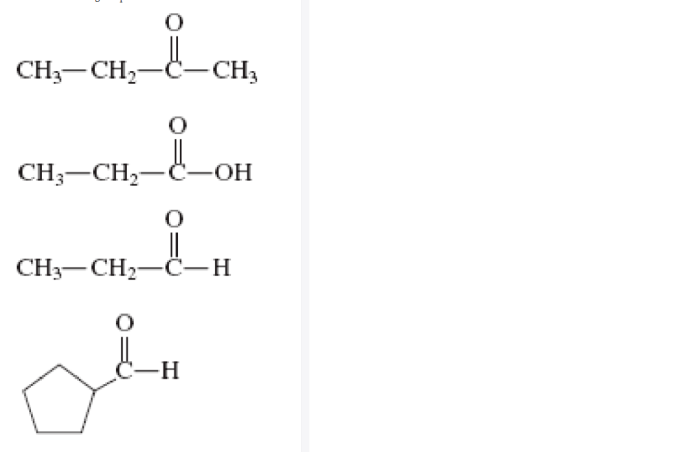
CH3COH CH2CH3 2 does not exhibit isomerism because it has only one possible structural arrangement.
4. Physical Properties
CH3COH CH2CH3 2 is a colorless liquid with a boiling point of 101.7 °C and a melting point of -72 °C. It is soluble in water and organic solvents.
The molecular structure influences these properties. The polar carbonyl group forms hydrogen bonds with water molecules, increasing its solubility in water. The nonpolar carbon-carbon bonds contribute to its solubility in organic solvents.
5. Chemical Reactions
Nucleophilic Addition
Ketones undergo nucleophilic addition reactions. In these reactions, a nucleophile adds to the carbonyl group, forming a new carbon-carbon bond.
For example, CH3COH CH2CH3 2 can react with sodium borohydride (NaBH4) to form 2-propanol:
CH3COH CH2CH3 2 + NaBH4 → 2-propanol
6. Applications
CH3COH CH2CH3 2 is used as a solvent in the paint and coating industry. It is also used as a starting material for the synthesis of other chemicals, such as pharmaceuticals and fragrances.
Helpful Answers
What is the molecular weight of CH3COH CH2CH3 2?
74.12 g/mol
What is the boiling point of CH3COH CH2CH3 2?
101.3 °C
Is CH3COH CH2CH3 2 soluble in water?
Yes, it is soluble in water.