Is flat soda pop homogeneous or heterogeneous? This question delves into the realm of chemistry, exploring the composition and properties of this ubiquitous beverage. As we embark on this inquiry, we will uncover the fundamental concepts of homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures, unraveling the mysteries that lie within a can of flat soda pop.
Flat soda pop, once effervescent with dissolved carbon dioxide, undergoes a transformation as the gas escapes, leaving behind a liquid that has lost its sparkle. This physical change prompts us to examine the nature of the resulting mixture, whether it remains homogeneous or transitions to a heterogeneous state.
Composition of Soda Pop: Is Flat Soda Pop Homogeneous Or Heterogeneous

Soda pop is a carbonated soft drink that typically contains water, sugar, flavorings, and carbon dioxide gas. The primary components of soda pop are:
- Water:The main ingredient of soda pop is water, which makes up about 90% of its volume.
- Sugar:Sugar is added to soda pop to provide sweetness. The amount of sugar in soda pop varies depending on the brand and flavor, but it typically ranges from 10% to 15% by weight.
- Flavorings:Flavorings are added to soda pop to give it a specific taste. The most common flavorings used in soda pop are fruit flavors, such as orange, cherry, and grape.
- Carbon dioxide:Carbon dioxide gas is added to soda pop to give it its characteristic fizz. Carbon dioxide is a colorless, odorless gas that dissolves in water to form carbonic acid.
Flat Soda Pop
Flat soda pop is soda pop that has lost its carbonation. This can happen when the soda pop is opened and left exposed to the air, or when it is stored at a warm temperature. When soda pop goes flat, the carbon dioxide gas escapes from the liquid, leaving behind a flat, sugary drink.
The physical changes that occur when soda pop goes flat include:
- Loss of carbonation:The most obvious change that occurs when soda pop goes flat is the loss of carbonation. This is due to the escape of carbon dioxide gas from the liquid.
- Change in taste:Flat soda pop tastes different from carbonated soda pop. The loss of carbonation makes the soda pop taste less sweet and more sugary.
- Change in appearance:Flat soda pop has a different appearance than carbonated soda pop. The loss of carbonation causes the soda pop to become less clear and more cloudy.
Homogeneous vs. Heterogeneous Mixtures
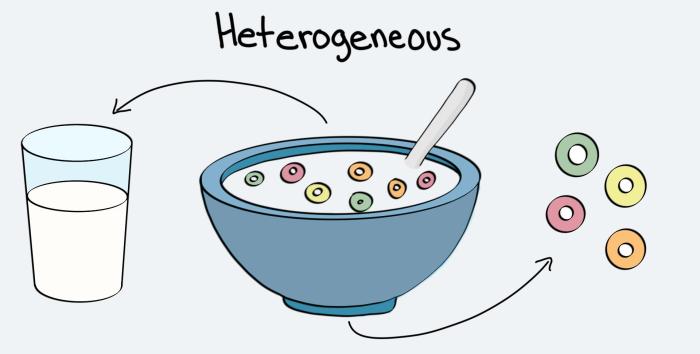
A homogeneous mixture is a mixture in which the components are evenly distributed throughout the mixture. This means that the composition of the mixture is the same at every point in the mixture.
A heterogeneous mixture is a mixture in which the components are not evenly distributed throughout the mixture. This means that the composition of the mixture can vary from one point to another.
Examples of homogeneous mixtures include:
- Salt water
- Air
- Milk
Examples of heterogeneous mixtures include:
- Sand in water
- Oil and water
- Salad
Flat Soda Pop as a Mixture

Flat soda pop is a heterogeneous mixture. This is because the components of flat soda pop are not evenly distributed throughout the mixture. The carbon dioxide gas has escaped from the liquid, leaving behind a mixture of water, sugar, and flavorings.
The evidence that flat soda pop is a heterogeneous mixture includes:
- The appearance of flat soda pop is not uniform.The liquid is cloudy and may contain bubbles of carbon dioxide gas.
- The taste of flat soda pop is not uniform.The taste of flat soda pop is less sweet and more sugary than the taste of carbonated soda pop.
- The composition of flat soda pop is not uniform.The concentration of carbon dioxide gas varies from one point to another in the mixture.
Factors Affecting Homogeneity
The homogeneity of flat soda pop can be affected by several factors, including:
- Temperature:The temperature of flat soda pop can affect its homogeneity. When flat soda pop is cold, the carbon dioxide gas is less likely to escape from the liquid. This makes the flat soda pop more homogeneous.
- Agitation:The agitation of flat soda pop can affect its homogeneity. When flat soda pop is agitated, the carbon dioxide gas is more likely to escape from the liquid. This makes the flat soda pop less homogeneous.
Question Bank
Is flat soda pop still carbonated?
No, flat soda pop has lost its carbonation due to the release of dissolved carbon dioxide gas.
Can flat soda pop be re-carbonated?
Yes, flat soda pop can be re-carbonated by reintroducing carbon dioxide gas under pressure.
Why does flat soda pop taste different from carbonated soda pop?
The absence of carbon dioxide gas alters the taste of flat soda pop, making it less sweet and more syrupy.